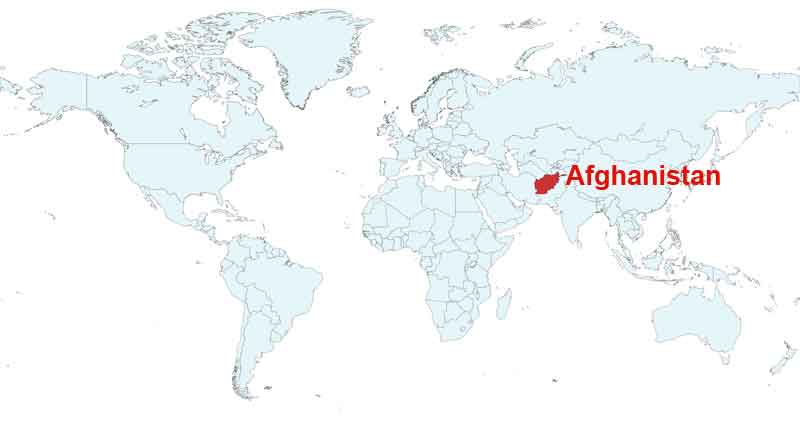
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a newly independent country located in South and Central Asia. It has a population of around 32 million, making it the 42nd most populous country in the world.
Afghanistan Bordering Countries:
- China
- Iran
- Pakistan
- Tajikistan
- Turkmenistan
- Uzbekistan
Regional Map
- Asia Map
- World map
Where is Afghanistan?
What to know
Names of cities in Afghanistan
Anar Darreh, Andkhvoy, Asadabad, Baghlan, Balamorghab, Balkh, Barak, Chaghcharan, Chah-e Ab, Charikar, Deh Shu, Delaram, Dowlatabad, Eshkashem, Farah, Farkhar, Feyzabad, Galalabad, Gardeyz, Ghazni, Herat (Hirat) Jalalabad , Kabzol (Kabul), Kadesh, Kajaki, Kandahar, Karokh, Keleft, Kholm, Khost, Kowt-e Ashrow, Kunduz, Lashkar Gah, Mahmud-e Raqi, Mazar-e Sharif, Mehtarlam, Meymaneh, Now Zad, Orgun, Qaleh -ye Now, Qalat, Qarah Bagh, Rostaq, Samangan, Sheberghan, Shindand, Spin Buldak, Taloqan, Tarin Kowt, Termez, Toktar, Towraghondi, Zaranji, Zareh Sharan.
Afghanistan Location
Paropamisus Range, Harirud River, Murghab River, Darya-ye Kondoz River, Harut River, Farah River, Khash River, Helmand River, Arghandab River, Amu Darya River, Hamun-e Saberi Lake, Gowd-e Zereh Lake, Abe Lake Istadeh -ye Moqor Lake, Barai Ghar Mountains, Shinkay Mountains, Rigestan Desert, Chagai Hills Mountains, Dasht-e Margow Desert.
Afghanistan Natural Resources
Afghanistan is rich in fossil fuel resources. Natural gas, oil, and coal are present in commercial quantities. Metal resources include copper, chromite, lead, zinc, and iron ore. Industrial minerals include talc, barite, sulfur, salt, precious and semiprecious gemstones.
Afghanistan’s Natural Hazards
Natural hazards in Afghanistan include floods and droughts. In addition, a destructive earthquake occurred in the Hindu Kush mountains.
Afghan Environmental Issues
Afghanistan has several environmental problems related to water. These include insufficient drinking water supplies and limited freshwater resources. Water and air pollution are also a problem. Soil and soil problems include overgrazing, desertification, land degradation, and deforestation. Much of the remaining forest continues to be cut down for fuel and building materials.